Contents
The Siege of Vicksburg (May 18 – July 4, 1863) was the final major military action in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Major General Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mississippi River and drove the Confederate Army of Mississippi, led by Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton, into the defensive lines surrounding the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, leading to the successful siege and Confederate surrender.
Vicksburg was the last major Confederate stronghold on the Mississippi River; therefore, capturing it completed the second part of the Northern strategy, the Anaconda Plan. When two major assaults against the Confederate fortifications, on May 19 and 22, were repulsed with heavy casualties, Grant decided to besiege the city beginning on May 25. After holding out for more than 40 days, with their supplies nearly gone, the garrison surrendered on July 4. The Vicksburg campaign's successful ending significantly degraded the Confederacy's ability to maintain its war effort. This action, combined with the surrender of the downriver Port Hudson to Major General Nathaniel P. Banks on July 9, yielded command of the Mississippi River to the Union forces, which held it for the rest of the conflict.
The Confederate surrender on July 4, 1863, is sometimes considered, combined with General Robert E. Lee's defeat at Gettysburg by Major General George Meade the previous day, the war's turning point. It cut off the Trans-Mississippi Department (containing the states of Arkansas, Texas and part of Louisiana) from the rest of the Confederate States, effectively splitting the Confederacy in two for the rest of the war. Lincoln called Vicksburg "the key to the war".[4]
Background
Military situation
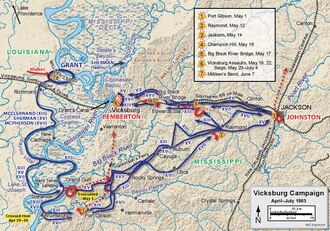
After crossing the Mississippi River south of Vicksburg at Bruinsburg and driving northeast, Grant won battles at Port Gibson and Raymond and captured Jackson, the Mississippi state capital, on May 14, 1863, forcing Pemberton to withdraw westward. Attempts to stop the Union advance at Champion Hill and Big Black River Bridge were unsuccessful. Pemberton knew that the corps under Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman was preparing to flank him from the north, and so had no choice but to withdraw or be outflanked. Pemberton burned the bridges over the Big Black River and devastated the countryside as he retreated to the well-fortified city of Vicksburg.[5]
The Confederates evacuated Hayne's Bluff, which was subsequently occupied by Sherman's cavalry on May 19, and Union steamboats no longer had to run the guns of Vicksburg, now being able to dock by the dozens up the Yazoo River. Grant could now receive supplies more directly than by the previous route, which ran through Louisiana, over the river crossing at Grand Gulf and Bruinsburg, then back up north.[5]
Over half of Pemberton's army had been lost in the two preceding battles[6] and many in Vicksburg expected General Joseph E. Johnston, in command of the Confederate Department of the West, to relieve the city—which he never did. Large numbers of Union troops were on the march to invest the city. They repaired the bridges over the Big Black River and crossed on May 18.[7] Johnston sent a note to his general, Pemberton, asking him to sacrifice the city and save his troops, something Pemberton would not do. Pemberton, a Northerner by birth, was probably influenced by his fear of public condemnation if he abandoned Vicksburg.[8]
Pemberton, trying to please Jefferson Davis, who insisted that Vicksburg and Port Hudson must be held, and to please Johnston, who thought both places worthless militarily, had been caught in the middle, a victim of a convoluted command system and his own indecisiveness. Too dispirited to think clearly, he chose to back his bedraggled army into Vicksburg rather than evacuate the city and head north where he might have escaped to campaign again. When he chose to take his army into Vicksburg, Pemberton sealed the fate of his troops and the city he had been determined to defend.
— Vicksburg, Michael B. Ballard.[9]
Fortifications
As the Union forces approached Vicksburg, Pemberton could put only 18,000 troops in his lines. Grant had over 35,000, with more on the way. However, Pemberton had the advantage of terrain and fortifications that made his defense nearly impregnable. The defensive line around Vicksburg ran for approximately six and a half miles (10 km), based on terrain of varying elevations that included hills and knobs with steep slopes which would require an attacker to ascend them under fire. The perimeter included many gun pits, forts, trenches, redoubts, and lunettes. The major fortifications of the line included: Fort Hill, on a high bluff north of the city; the Stockade Redan, dominating the approach to the city on Graveyard Road from the northeast; the 3rd Louisiana Redan; the Great Redoubt; the Railroad Redoubt, protecting the gap for the railroad line entering the city; the Square Fort (Fort Garrott); a salient along the Hall's Ferry Road; and the South Fort.[10]
Opposing forces
| Army Commanders at Vicksburg |
|---|
Union
Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's Union Army of the Tennessee brought five corps to the siege:
- IX Corps,[11] under Maj. Gen. John Parke;
- XIII Corps, under Maj. Gen. John A. McClernand;
- XV Corps, under Maj. Gen. William T. Sherman;
- XVI Corps (detachment), under Maj. Gen. Cadwallader C. Washburn;
- XVII Corps, under Maj. Gen. James B. McPherson.
Confederate
Lt. Gen. John C. Pemberton's Confederate Army of Mississippi inside the Vicksburg line consisted of four divisions, under Maj. Gens.:
Siege
Assaults
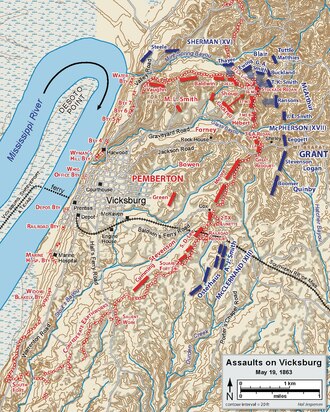

Grant wanted to overwhelm the Confederates before they could fully organize their defenses and ordered an assault against the Stockade Redan for May 19. Troops from Sherman's corps had a difficult time approaching the position under rifle and artillery fire from the 36th Mississippi Infantry, Brig. Gen. Louis Hébert's brigade. They had to negotiate a steep ravine protected by abatis and cross a 6-foot-deep (1.8 m), 8-foot-wide (2.4 m) ditch before attacking the 17-foot-high (5.2 m) walls of the redan. This first attempt was easily repulsed. Grant ordered an artillery bombardment to soften the defenses and at about 2 pm, Sherman's division under Maj. Gen. Francis P. Blair tried again, but only a small number of men were able to advance even as far as the ditch below the redan. The assault collapsed in an exchange of rifle fire and hand grenades lobbing back and forth.[12]
The failed Union assaults of May 19 damaged troop morale, deflating the confidence the soldiers had felt after their string of victories across Mississippi. They were also costly, with 157 killed, 777 wounded, and eight missing, versus Confederate casualties of eight killed and 62 wounded. The Confederates, assumed to be demoralized, had regained their fighting edge.[13]
Grant planned another assault for May 22, but this time with greater care; his troops would first reconnoiter thoroughly and soften up the defenses with artillery and naval gunfire. The lead units were supplied with ladders to ascend the fortification walls. Grant did not want a long siege, and this attack was to be by the entire army across a wide front.[14]
Despite their bloody repulse on May 19, Union troops were in high spirits, now well-fed with provisions they had foraged. On seeing Grant pass by, a soldier commented, "Hardtack". Soon all Union troops in the vicinity were yelling, "Hardtack! Hardtack!" The Union served hardtack, beans, and coffee the night of May 21. Everyone expected that Vicksburg would fall the next day.[15]
Union forces bombarded the city all night, from 220 artillery pieces and with naval gunfire from Rear Adm. David D. Porter's fleet in the river. While causing little property damage, they damaged Confederate civilian morale. On the morning of May 22, the defenders were bombarded again for four hours before the Union attacked once more along a 3-mile (5 km) front at 10 am.[16]
Sherman attacked once again down the Graveyard Road, with 150 volunteers (nicknamed the forlorn hope detachment) leading the way with ladders and planks, followed by the divisions of Blair and Brig. Gen. James M. Tuttle, arranged in a long column of regiments. They hoped to achieve a breakthrough by concentrating their mass on a narrow front. They were driven back in the face of heavy rifle fire. Blair's brigades under Cols. Giles A. Smith and T. Kilby Smith made it as far as a ridge 100 yards from Green's Redan, the southern edge of the Stockade Redan, from where they poured heavy fire into the Confederate position, but to no avail. Tuttle's division, waiting its turn to advance, did not have an opportunity to move forward. On Sherman's far right, the division of Brig. Gen. Frederick Steele spent the morning attempting to get into position through a ravine of the Mint Spring Bayou.[17]
McPherson's corps was assigned to attack the center along Jackson Road. On their right flank, the brigade of Brig. Gen. Thomas E. G. Ransom advanced to within 100 yards of the Confederate line, but halted to avoid dangerous flanking fire from Green's Redan. On McPherson's left flank, the division of Maj. Gen. John A. Logan was assigned to assault the 3rd Louisiana Redan and the Great Redoubt. The brigade of Brig. Gen. John E. Smith made it as far as the slope of the redan, but huddled there, dodging grenades until dark, when they were recalled. Brig. Gen. John D. Stevenson's brigade advanced in two columns against the redoubt, but their attack also failed when they found their ladders were too short to scale the fortification. Brig. Gen. Isaac F. Quinby's division advanced a few hundred yards, but halted for hours while its generals engaged in confused discussions.[18]
On the Union left, McClernand's corps moved along the Baldwin Ferry Road and astride the Southern Railroad of Mississippi. The division of Brig. Gen. Eugene A. Carr was assigned to capture the Railroad Redoubt and the 2nd Texas Lunette; the division of Brig. Gen. Peter J. Osterhaus was assigned the Square Fort. Carr's men achieved a small breakthrough at the 2nd Texas Lunette and requested reinforcements.[19]
By 11 am, it was clear that a breakthrough was not forthcoming and that the advances by Sherman and McPherson were failures. Just then, Grant received a message from McClernand, which stated that he was heavily engaged, the Confederates were being reinforced, and he requested a diversion on his right from McPherson's corps. Grant initially refused the request, telling McClernand to use his own reserve forces for assistance; Grant was mistakenly under the impression that McClernand had been lightly engaged and McPherson heavily, although the reverse was true. McClernand followed up with a message that was partially misleading, implying that he had captured two forts—"The Stars and Stripes are flying over them."—and that another push along the line would achieve victory for the Union Army. In fact, more than a dozen members of the 22nd Iowa Infantry Regiment had secured a tenuous foothold in a portion of the fortification known as the Railroad Redoubt, and forced Confederate defenders back from that point, though the Iowans could not advance further. Although Grant once again demurred, he showed the dispatch to Sherman, who ordered his own corps to advance again. Grant, reconsidering, then ordered McPherson to send Quinby's division to aid McClernand.[20]
As our line of battle started and before our yell had died upon the air the confederate fortifications in our front were completely crowded with the enemy, who with an answering cry of defiance, poured into our ranks, one continuous fire of musketry, and the forts and batteries in our front and both sides, were pouring in to our line, an unceasing fire of shot and shell, with fearful results, as this storm of fire sent us, intermixed with the bursting shells and that devilish rebel yell, I could compare to nothing but one of Dante's pictures of Hell, a something too fearful to describe.
Daniel A. Ramsdell, Ransom's Brigade[21]
Sherman ordered two more assaults. At 2:15 pm, Giles Smith and Ransom moved out and were repulsed immediately. At 3 pm, Tuttle's division suffered so many casualties in their aborted advance that Sherman told Tuttle, "This is murder; order those troops back." By this time, Steele's division had finally maneuvered into position on Sherman's right, and at 4 pm, Steele gave the order to charge against the 26th Louisiana Redoubt. They had no more success than any of Sherman's other assaults.[22]
In McPherson's sector, Logan's division made another thrust down the Jackson Road at about 2 pm, but met with heavy losses and the attack was called off. McClernand attacked again, reinforced by Quinby's division, but with no success. Union casualties for the day totalled 502 killed, 2,550 wounded, and 147 missing, about evenly divided across the three corps. Confederate casualties were not reported directly, but are estimated to have been under 500. Grant blamed McClernand's misleading dispatches for part of the poor results of the day, storing up another grievance against the political general who had caused him so many aggravations during the campaign.[23]
Siege operations
Historian Shelby Foote wrote that Grant "did not regret having made the assaults; he only regretted that they had failed."[24] Grant reluctantly settled into a siege. On May 25, Lt. Col. John A. Rawlins issued Special Orders No. 140 for Grant:
Corps Commanders will immediately commence the work of reducing the enemy by regular approaches. It is desirable that no more loss of life shall be sustained in the reduction of Vicksburg, and the capture of the Garrison. Every advantage will be taken of the natural inequalities of the ground to gain positions from which to start mines, trenches, or advance batteries. ...[25]
Grant wrote in his memoirs, "I now determined upon a regular siege—to 'out-camp the enemy,' as it were, and to incur no more losses."[26]
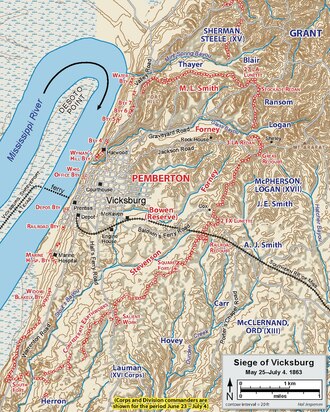
When the Federal troops started to dig in, they built complicated defenses that soldiers at the time called "ditches." These went all the way around the city and got closer and closer to the Confederate defenses. With their backs against the Mississippi and Union gunboats firing from the river, Confederate soldiers and citizens alike were trapped. Pemberton was determined to hold his few miles of the Mississippi as long as possible, hoping for relief from Johnston or elsewhere.[27]
A new problem confronted the Confederates. The dead and wounded of Grant's army lay in the heat of Mississippi summer, the odor of the deceased men and horses fouling the air, the wounded crying for medical help and water. Grant first refused a request of truce, thinking it a show of weakness. Finally he relented, and the Confederates held their fire while the Union recovered the wounded and dead on May 25, soldiers from both sides mingling and trading as if no hostilities existed for the moment.[28]
After this truce, Grant's army began to fill the 12-mile (19 km) ring around Vicksburg. It soon became clear that even 50,000 Union soldiers would not be able to effect a complete encirclement of the Confederate defenses. Pemberton's outlook on escape was pessimistic, but there were still roads leading south out of Vicksburg unguarded by Union troops. Grant sought help from Maj. Gen. Henry W. Halleck, the Union general-in-chief. Halleck quickly began to shift Union troops in the West to meet Grant's needs. The first of these reinforcements was a 5,000-man division from the Department of the Missouri under Maj. Gen. Francis J. Herron on June 11. Herron's troops, remnants of the Army of the Frontier, were attached to McPherson's corps and took up position on the far south. Next came a three division detachment from XVI Corps led by Brig. Gen. Cadwallader C. Washburn on June 12, assembled from troops at the nearby posts of Corinth, Memphis, and LaGrange. The final significant group of reinforcements to join was the 8,000-man strong IX Corps from the Department of the Ohio, led by Maj. Gen. John G. Parke, arriving on June 14. With the arrival of Parke, Grant had 77,000 men around Vicksburg.[29]
In an effort to cut Grant's supply line, Confederates in Louisiana under Major General John G. Walker attacked Milliken's Bend up the Mississippi on June 7. This was largely defended by recently enlisted United States colored troops. Despite having inferior weaponry, they fought bravely and repulsed the Confederates with help from gunboats, although at heavy cost; the defenders lost 652 to the Confederate 185. The loss at Milliken's Bend left the Confederates with no hope for relief other than from the cautious Johnston.[30]
We have our trenches pulled up so close to the enemy that we can throw hand grenades over into their forts. The enemy do not dare show their heads above the parapet at any time, so close and so watchful are our sharpshooters. The town is completely invested. My position is so strong that I feel myself abundantly able to leave it so and go out twenty or thirty miles with force enough to whip two such garrisons.
Ulysses S. Grant, writing to George G. Pride, June 15, 1863[31]
Pemberton was boxed in with plentiful munitions but little food. The poor diet was telling on the Confederate soldiers. By the end of June, half were sick or hospitalized. Scurvy, malaria, dysentery, diarrhea, and other diseases cut their ranks. At least one city resident had to stay up at night to keep starving soldiers out of his vegetable garden. The constant shelling did not bother him as much as the loss of his food. As the siege wore on, fewer and fewer horses, mules, and dogs were seen wandering about Vicksburg. Shoe leather became a last resort of sustenance for many adults.[32]

During the siege, Union gunboats lobbed over 22,000 shells into the town and army artillery fire was even heavier. As the barrages continued, suitable housing in Vicksburg was reduced to a minimum. A ridge, located between the main town and the rebel defense line, provided lodging for the duration. Over 500 caves, known locally as "bombproofs", were dug into the yellow clay hills of Vicksburg. Whether houses were structurally sound or not, it was deemed safer to occupy these dugouts. People did their best to make them comfortable, with rugs, furniture, and pictures. They tried to time their movements and foraging with the rhythm of the cannonade, sometimes unsuccessfully. Because of the citizens' burrowing, the Union soldiers gave the town the nickname of "Prairie Dog Village". Despite the ferocity of the Union fire, fewer than a dozen civilians are known to have been killed during the siege.[33]
Command changes
One of Grant's actions during the siege was to settle a lingering rivalry. On May 30, General McClernand wrote a self-adulatory note to his troops, claiming much of the credit for the soon-to-be victory. Grant had been waiting six months for him to slip, ever since they clashed early in the campaign, around the Battle of Arkansas Post. He had received permission to relieve McClernand in January 1863 but waited for an unequivocal provocation; McClernand was relieved on June 18. Grant so carefully prepared his action that McClernand was left without recourse. McClernand's XIII Corps was turned over to Maj. Gen. Edward Ord, who had recovered from an October 1862 wound sustained at Hatchie's Bridge. In May 1864, McClernand would be given a command in a remote area of Texas.[34]
Another command change occurred on June 22. In addition to Pemberton in Vicksburg, Grant had to be aware of Confederate forces in his rear under the command of Joseph E. Johnston. He stationed one division in the vicinity of the Big Black River Bridge and another reconnoitered as far north as Mechanicsburg; both acted as covering forces. By June 10, the IX Corps, under Maj. Gen. John G. Parke, was transferred to Grant's command. This corps became the nucleus of a special task force whose mission was to prevent Johnston, who was gathering his forces at Canton, from interfering with the siege. Sherman was given command of this task force and Brig. Gen. Frederick Steele replaced him at XV Corps. Johnston eventually began moving to relieve Pemberton and reached the Big Black River on July 1, but he delayed a potentially difficult encounter with Sherman until it was too late for the Vicksburg garrison, and then fell back to Jackson.[35] Sherman would pursue Johnston and recapture Jackson on July 17.
Louisiana operations
Throughout the siege Union and Confederate forces kept busy in a supporting role on the Louisiana side of the Mississippi River. Lt. Gen. Edmund Kirby Smith, commander of the Trans-Mississippi Department, received a telegraph from Pemberton on May 9 requesting that he move against Grant's communication lines along the Mississippi River. Grant had established important supply depots at Milliken's Bend, Young's Point, and Lake Providence, all within Smith's jurisdiction, but Smith failed to recognize the importance of Pemberton's situation. It was not until June when Smith finally took action on Pemberton's request, directing Maj. Gen. Richard Taylor to "do something" in support of the Vicksburg garrison.[36] Taylor commanded the District of Western Louisiana and developed a three-pronged campaign against Grant's three supply depots. All three of Taylor's assaults were defeated at the Battle of Milliken's Bend, the Battle of Young's Point, and the Battle of Lake Providence.
In response to the growing Confederate activity in the area, Grant decided to dispatch troops from the Vicksburg trenches across the river. The presence of Maj. Gen. John G. Walker's Confederate division on the Louisiana side was of particular concern; its presence could possibly aid any Confederate attempt to escape from Vicksburg. Therefore, Brig. Gen. Alfred W. Ellet's Mississippi Marine Brigade and Joseph A. Mower's brigade from Sherman's corps were ordered to the vicinity of Milliken's Bend. Mower and Ellet were to cooperate against Walker's division, which was stationed in the vicinity of Richmond, Louisiana. Richmond was also an important supply line providing Vicksburg with food from Louisiana. On June 15, Ellet and Mower defeated Walker and destroyed Richmond.[37]
Ellet's men returned to De Soto Point and constructed an artillery battery targeting an iron foundry recasting spent Union artillery shells. Construction was begun on June 19, which placed a 20-pounder Parrott rifle in a casemate of railroad iron. The targeted foundry was destroyed on June 25 and the next day a second Parrott gun was added to the battery, which continued to harass the defenders until the garrison's surrender.[38]
Additional Confederate activity in Louisiana occurred on June 29 at Goodrich's Landing when they attacked a plantation and an army training center run by former slaves. The Confederates destroyed the plantations and captured over a hundred former slaves before disengaging in the face of Ellet's Marines. Confederate raids such as these were disruptive and caused damage, but they were only minor setbacks and demonstrated that the Confederates could cause only momentary disturbances in the area.[39]
Crater at the Third Louisiana Redan

Late in the siege, Union troops tunneled under the 3rd Louisiana Redan and packed the mine with 2,200 pounds of gunpowder. The explosion blew apart the Confederate lines on June 25, while an infantry attack made by troops from Logan's XVII Corps division followed the blast. The 45th Illinois Regiment (known as the "Lead Mine Regiment"), under Col. Jasper A. Maltby, charged into the 40-foot (12 m) diameter, 12-foot (3.7 m) deep crater with ease, but were stopped by recovering Confederate infantry. The Union soldiers became pinned down and the defenders rolled artillery shells with short fuses into the pit with deadly results. Union engineers worked to set up a casemate in the crater in order to extricate the infantry, and soon the soldiers fell back to a new defensive line. From the crater left by the explosion, Union miners worked to dig a new mine to the south. On July 1, this mine was detonated but no infantry attack followed. Pioneers worked throughout July 2 and 3 to widen the initial crater to be large enough for an infantry column of four to pass through for any future assault. However, events the following day negated the need for any further assaults.[40]
Capture

On July 3, Pemberton sent a note to Grant regarding the possibility of negotiations for peace. Grant, as he had done at Fort Donelson, first demanded unconditional surrender. He then reconsidered, not wanting to feed 30,000 Confederates in Union prison camps, and offered to parole all prisoners. Considering their destitute and starving state, he never expected them to fight again; he hoped they would carry home the stigma of defeat to the rest of the Confederacy. In any event, shipping that many prisoners north would have occupied his army and taken months.[41] Pemberton officially surrendered his army on July 4.[42] Most of the men who were paroled on July 6 were exchanged and received back into the Confederate Army on August 4, 1863, at Mobile Harbor, Alabama. They were back in Chattanooga, Tennessee, by September and some fought in the Battles for Chattanooga in November and against Sherman's invasion of Georgia in May 1864. The Confederate government protested the validity of the paroles on technical grounds and the issue was referred to Grant who, in April 1864, was general in chief of the army. The dispute effectively ended all further prisoner exchanges during the war except for hardship cases.[43] When the captured 26th, 27th, 29th, and 31st Louisiana Infantry Regiments were exchanged in 1863 and 1864, many of the paroled soldiers failed to report for duty and remained at their homes. Those Louisianans who returned to active duty were never again used in combat.[44]
Surrender was formalized by an old oak tree, "made historical by the event". In his Personal Memoirs, Grant described the fate of this luckless tree:
It was but a short time before the last vestige of its body, root and limb had disappeared, the fragments taken as trophies. Since then the same tree has furnished as many cords of wood, in the shape of trophies, as the 'True Cross'.[45]

The surrender was finalized on July 4, Independence Day, a day Pemberton had hoped would bring more sympathetic terms from the United States. Although the Vicksburg campaign continued with some minor actions, the fortress city had fallen and, with the surrender of Port Hudson on July 9, the Mississippi River was firmly in Union hands and the Confederacy split in two. President Lincoln famously announced, "The Father of Waters again goes unvexed to the sea."[46]
Union casualties for the battle and siege of Vicksburg were 4,835; Confederate were 32,697, of whom 29,495 had surrendered.[3] The full campaign, since March 29, claimed 10,142 Union and 9,091 Confederate killed and wounded. In addition to the men under his command, Pemberton turned over to Grant 172 cannons and 50,000 rifles.[47]
Aftermath
Vicksburg was the last major Confederate stronghold on the Mississippi River; therefore, capturing it completed the second part of the Northern strategy, the Anaconda Plan. The successful ending of the Vicksburg campaign significantly degraded the ability of the Confederacy to maintain its war effort. This action, combined with the surrender of Port Hudson to Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks on July 9, yielded command of the Mississippi River to the Union forces, who would hold it for the rest of the conflict.
The Confederate surrender at 10:00 AM on July 4, 1863, is sometimes considered, when combined with Gen. Robert E. Lee's July 3 defeat at Gettysburg by Maj. Gen. George Meade, the turning point of the war. It cut off the states of Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas from the rest of the Confederate States, effectively splitting the Confederacy in two for the duration of the war. The Union victory also permanently severed communication between the Trans-Mississippi Department and the balance of the Confederacy.[48]
Folk tradition holds that the Fourth of July (Independence Day) holiday was not celebrated by Vicksburg until World War II.[49] This claim is inaccurate, for large Independence Day celebrations were held as early as 1907.[50]
Battlefield preservation
The works around Vicksburg are now maintained by the National Park Service as part of Vicksburg National Military Park. The park, located in Vicksburg, Mississippi, and Delta, Louisiana (flanking the Mississippi River), also commemorates the greater Vicksburg campaign which led up to the battle and includes reconstructed forts and trenches. The park includes 1,325 historic monuments and markers, 20 miles (32 km) of historic trenches and earthworks, a 16-mile (26 km) tour road, a 12.5-mile (20 km) walking trail, two antebellum homes, 144 emplaced cannons, the restored gunboat USS Cairo (sunk on December 12, 1862, on the Yazoo River), and the Grant's Canal site, where the Union Army attempted to build a canal to let their ships bypass Confederate artillery fire.
The American Battlefield Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved more than 46 acres (0.19 km2) of the Vicksburg battlefield through mid-2023.[51]
In early 2020, torrential rainfalls caused catastrophic damage to Vicksburg National Military Park. Erosion caused by the region's unique geology has been an ongoing issue for the park over the decades, but this event was devastating, undermining large swaths of the hilly landscape, buckling miles of the park's roads and washing out portions of Vicksburg National Cemetery, endangering the remains.[52]
See also
- Troop engagements of the American Civil War, 1863
- List of costliest American Civil War land battles
- Commemoration of the American Civil War
- Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps
- Armies in the American Civil War
- Mississippi River in the American Civil War
Notes
- ^ See: Rawley, pp. 145–169.
- ^ Kennedy, p. 172.
- ^ a b c Kennedy, p. 173.
- ^ "History & Culture – Vicksburg National Military Park (U.S. National Park Service)". www.nps.gov. Retrieved January 14, 2021.
- ^ a b Esposito, text for map 105.
- ^ Kennedy, pp. 171.
- ^ National Park Service. Grant's army arrived at the outskirts of Vicksburg on May 19, but formal siege operations began with Grant's Special Order No. 140 on May 25 (Simon, p. 267).
- ^ Smith, p. 251; Grabau, pp. 343–346; Catton, pp. 198–200; Esposito, text for map 106.
- ^ Ballard, p. 318.
- ^ Eicher, pp. 467–468.
- ^ IX Corps: joined from the Department of the Ohio, June 14 to 17.
- ^ Eicher, p. 468; Ballard, pp. 327–332.
- ^ Bearss, vol. III, pp. 778–780; Ballard, p. 332.
- ^ Ballard, p. 339.
- ^ Ballard, p. 333.
- ^ Kennedy, p. 171; Foote, p. 384; Smith, p. 252.
- ^ Ballard, pp. 338–339; Bearss, vol. III, pp. 815–819.
- ^ Ballard, pp. 339–340; Bearss, vol. III, pp. 819–823.
- ^ Ballard, pp. 340–343.
- ^ Ballard, pp. 343–344; Bearss, vol. III, pp. 836–838.
- ^ Ballard, pp. 344–345.
- ^ Ballard, pp. 344–346.
- ^ Eicher, p. 469; Bearss, vol. III, p. 869; Kennedy, p. 172.
- ^ Foote, p. 386.
- ^ Simon, pp. 267–268.
- ^ Grant, ch. XXXVII, p. 1.
- ^ Smith, p. 253; Foote, p. 412; Catton, p. 205.
- ^ Bearss, vol. III, pp. 860–861; Foote, p. 387.
- ^ Bearss, vol. III, pp. 963, 1071–1079.
- ^ "Milliken's Bend", National Park Service (NPS) https://web.archive.org/web/20140814001420/http://www.nps.gov/history/hps/abpp/battles/la011.htm; Bearss, vol. III, pp. 1175–1187.
- ^ Bearss, vol. III, p. 875.
- ^ Korn, pp. 149–152; Catton, p. 205; Ballard, pp. 385–386.
- ^ Korn, p. 139; Foote, p. 412.
- ^ Bearss, vol. III, pp. 875–879; Ballard, pp. 358–359; Korn, pp. 147–148.
- ^ Esposito, text for map 107.
- ^ "Vicksburg NMP: Young's Point". Nps.gov. Retrieved May 18, 2013.
- ^ "Vicksburg NMP: Battle of Richmond". Nps.gov. Retrieved May 18, 2013.
- ^ "Vicksburg NMP: US Mississippi Marine Brigade". Nps.gov. Retrieved May 18, 2013.
- ^ "ABPP: Goodrich's Landing". Nps.gov. Archived from the original on January 6, 2008. Retrieved May 18, 2013.https://web.archive.org/web/20140102043148/http://www.nps.gov/history/hps/abpp//battles/la014.htm
- ^ Grabau, pp. 428–438; Bearss, vol. III, pp. 908–930.
- ^ Smith, pp. 254–255.
- ^ "Vicksburg". Civil War Trust. Retrieved August 21, 2016.
- ^ Henderson, Lillian, The Roster of Confederate Soldiers of Georgia, Longino and Porter, 1994; Bearss, vol III, pp. 1309–1311.
- ^ Bergeron 1989, pp. 135–143.
- ^ Grant, ch. XXXVIII, p. 16.
- ^ McPherson, p. 638.
- ^ Ballard, pp. 398–399.
- ^ Vicksburg Campaign; History.com online website; text: "...The Siege of Vicksburg (May 18, 1863 – July 4, 1863) was a decisive Union victory during the American Civil War (1861–65) ..."; accessed June 2020
- ^ Historian Michael G. Ballard, in his Vicksburg campaign history, pp. 420–421, claims that this story has little foundation in fact. Although it is unknown whether city officials sanctioned the day as a local holiday, Southern observances of July 4 were for many years characterized more by family picnics than by formal city or county activities.
- ^ Waldrep, Christopher (2005). Vicksburg's Long Shadow: The Civil War Legacy of Race and Remembrance. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 247. ISBN 978-0742548688.
- ^ "Vicksburg Battlefield". American Battlefield Trust. Retrieved June 20, 2023.
- ^ [1] American Battlefield Trust "Erosion Undermines History at Vicksburg National Military Park" webpage. Accessed May 12, 2023.
References
- Ballard, Michael B. Vicksburg, The Campaign that Opened the Mississippi. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2004. ISBN 0-8078-2893-9.
- Bearss, Edwin C. The Campaign for Vicksburg. 3 vols. Dayton, OH: Morningside House, 1985. ISBN 978-0-89029-312-6.
- Catton, Bruce. The Centennial History of the Civil War. Vol. 3, Never Call Retreat. Garden City, NY: Doubleday, 1965. ISBN 0-671-46990-8.
- Eicher, David J. The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. ISBN 0-684-84944-5.
- Esposito, Vincent J. West Point Atlas of American Wars. New York: Frederick A. Praeger, 1959. OCLC 5890637. The collection of maps (without explanatory text) is available online at the West Point website.
- Foote, Shelby. The Civil War: A Narrative. Vol. 2, Fredericksburg to Meridian. New York: Random House, 1958. ISBN 0-394-49517-9.
- Gabel, Christopher R., Staff ride handbook for the Vicksburg Campaign, December 1862 – July 1863. Fort Leavenworth, Kan.: Combat Studies Institute Press, 2001. OCLC 47296103.
- Grabau, Warren E. Ninety-Eighty Days: A Geographer's View of the Vicksburg Campaign. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2000. ISBN 1-57233-068-6.
- Grant, Ulysses S. (1885). Personal Memoirs of U.S. Grant. Vol. I. Vol. I. New York: Charles L. Webster & Company. p. 612. OCLC 44674220.
- Grant, Ulysses S. (1892). Personal Memoirs of U.S. Grant. Vol. II. Vol. II. New York: Charles L. Webster & Company. p. 660. OCLC 44674220.
- Kennedy, Frances H., ed. The Civil War Battlefield Guide Archived December 30, 2017, at the Wayback Machine. 2nd ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co., 1998. ISBN 0-395-74012-6.
- Korn, Jerry, and the Editors of Time-Life Books. War on the Mississippi: Grant's Vicksburg Campaign. Alexandria, VA: Time-Life Books, 1985. ISBN 0-8094-4744-4.
- McPherson, James M. Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era. Oxford History of the United States. New York: Oxford University Press, 1988. ISBN 0-19-503863-0.
- Silkenat, David. Raising the White Flag: How Surrender Defined the American Civil War. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2019. ISBN 978-1-4696-4972-6.
- Smith, Jean Edward. Grant. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. ISBN 0-684-84927-5.
- Simon, John Y., ed. The Papers of Ulysses S. Grant. Vol. 8, April 1 – July 6, 1863. Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press, 1979. ISBN 0-8093-0884-3.
- National Park Service battle description
- CWSAC Report Update
- Various resources from the University Libraries Division of Special Collections, The University of Alabama.
- U.S. War Department, The War of the Rebellion: a Compilation of the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1880–1901.
Further reading
- Ballard, Michael B. Grant at Vicksburg: The General and the Siege. Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press, 2013. ISBN 978-0-8093-3240-3.
- Bearss, Edwin C. Receding Tide: Vicksburg and Gettysburg: The Campaigns That Changed the Civil War. Washington, DC: National Geographic Society, 2010. ISBN 978-1-4262-0510-1.
- Bergeron, Arthur W. Jr. (1989). Guide to Louisiana Confederate Military Units 1861–1865. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 0-8071-2102-9.
- Groom, Winston. Vicksburg, 1863. New York: Knopf, 2009. ISBN 978-0-307-26425-1.
- Miller, Donald L. Vicksburg: Grant's Campaign that Broke the Confederacy. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2019. ISBN 978-1-4516-4137-0.
- Rawley, James A. (1966). Turning Points of the Civil War. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 0-8032-8935-9. OCLC 44957745.
- Shea, William L. and Terrence J. Winschel. Vicksburg is the Key: The Struggle for the Mississippi River. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 2003. ISBN 978-0-8032-9344-1.
- Solonick, Justin S. (2015). Engineering Victory: The Union Siege of Vicksburg. Southern Illinois University Press. ISBN 978-0-8093-3392-9.
- Winschel, Terrence J. Triumph & Defeat: The Vicksburg Campaign. Campbell, CA: Savas Publishing Company, 1999. ISBN 1-882810-31-7.
- Winschel, Terrence J. Triumph & Defeat: The Vicksburg Campaign, Vol. 2. New York: Savas Beatie, 2006. ISBN 1-932714-21-9.
- Winschel, Terrence J. Vicksburg: Fall of the Confederate Gibraltar. Abilene, TX: McWhiney Foundation Press, 1999. ISBN 978-1-893114-00-5.
- Woodworth, Steven E.ed. Grant's Lieutenants: From Cairo to Vicksburg. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 2001. ISBN 0-7006-1127-4.
- Woodworth, Steven E. Jefferson Davis and His Generals: The Failure of Confederate Command in the West. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1990. ISBN 0-7006-0461-8.
- Woodworth, Steven E. Nothing but Victory: The Army of the Tennessee, 1861–1865. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2005. ISBN 0-375-41218-2.
External links
- Vicksburg Campaign animated map, American Battlefield Trust
- Vicksburg Virtual Museum Exhibit, National Park Service
- A Minecraft simulation of the siege of Vicksburg, American Battlefield Trust
- C-SPAN American History TV Tour of Vicksburg National Military Park



