Contents
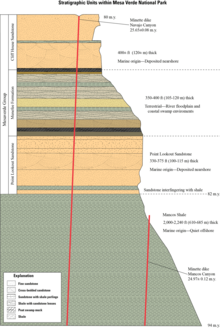
The Point Lookout Sandstone is a Cretaceous bedrock formation occurring in New Mexico and Colorado.
Description
The formation consists of two informal members. The lower is a sequence of thinly bedded sandstone and shale,[1] while the upper is a massive medium- to fine-grained cross-bedded sandstone, light gray to buff in color, that is a conspicuous cliff-forming unit.[1][2] Maximum thickness is 131 meters (430 feet).[1]
The lower contact is placed at the first thin sandstone bed above the shale of the Mancos Shale. The formation is overlain by the Menefee Formation.[1]
The Point Lookout Sandstone was deposited in the Cretaceous Interior Seaway, as part of a regressive sequence as the seaway was receding. It is transitional between the marine environment of the underlying Mancos and the coastal plain environment of the overlying Menefee Formation.
Fossils
Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus.[3]
The ammonite Clioscaphites vermiformis was identified in the formation.[4]
Resource geology
Exposures of the Point Lookout Sandstone at Apache Mesa in New Mexico contain heavy mineral deposits, rich in titanium, zirconium, rare earth elements, and other valuable metals. However, the deposits are much too small to be economical to mine as of 2021. The deposits represent a beach placer deposit similar to ones seen in the southeastern U.S. Atlantic coast, southeastern Australia, and India.[5]
History of investigation
The sandstone was first described by A. J. Collier for exposures in cliffs at Point Lookout, in Mesa Verde National Park, Montezuma County, Colorado, in the Paradox Basin,[6] and later described by Allen and Balk in 1954 as part of the Mesaverde Group in the San Juan Basin in New Mexico.[7]
See also
Footnotes
References
- Allen, J.E.; Balk, Robert (1954). "Mineral Resources of Fort Defiance and Tohatchi quadrangles, Arizona and New Mexico". New Mexico Bureau of Mines and Mineral Resources Bulletin. 36. Retrieved 25 March 2021.
- Cather, Steven (2010). "Preliminary geologic map of the San Lucas Dam quadrangle, McKinley County, New Mexico". New Mexico Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Open-File Geologic Map. OF-GM 212. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- Collier, A.J. (1919). "Coal south of Mancos, Montezuma County, Colorado". Contributions to Economic Geology, 1918; Part 2, Mineral Fuels: U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin. 691-K: K293–K310. doi:10.3133/b691K.
- Lucas, Spencer G.; Heckert, Andrew B. (2005). "Mesozoic stratigraphy at Durango, Colorado" (PDF). New Mexico Geological Society Field Conference Series. 56. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- McLemore, V.T. (2017). "Heavy mineral, beach-placer sandstone deposits at Apache Mesa, Jicarilla Apache Reservation, Rio Arriba County, New Mexico" (PDF). New Mexico Geological Society Field Conference Series. 68: 123–132. Retrieved 25 March 2021.
- Tschudy, R.H. (1976). "Palynology of Crevasse Canyon and Menefee Formation of San Juan basin, New Mexico" (PDF). In Beaumont, E.C.; Shomaker, J.W.; Stone, W.J. (eds.). Guidebook to coal geology of northwest New Mexico: New Mexico Bureau of Mines and Mineral Resources Circular. Vol. 154. pp. 48–55. Retrieved 25 March 2021.
- Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; Osmólska, Halszka (2004). The Dinosauria (2nd ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.

