Contents
Nahcolite is a soft, colourless or white carbonate mineral with the composition of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) also called thermokalite. It crystallizes in the monoclinic system.[4]
Nahcolite was first described in 1928 for an occurrence in a lava tunnel at Mount Vesuvius, Italy.[2] Its name refers to the elements which compose it: Na, H, C, and O.[5] It occurs as a hot spring and saline lake precipitate or efflorescence; in differentiated alkalic massifs; in fluid inclusions as a daughter mineral phase and in evaporite deposits.[2][4]
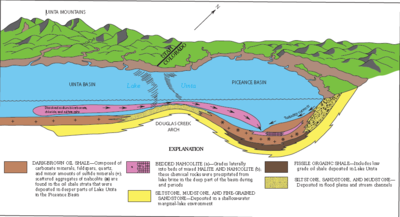
It occurs in association with trona, thermonatrite, thenardite, halite, gaylussite, burkeite, northupite and borax.[3] It has been reported in a Roman conduit at Stufe de Nerone, Campi Flegrei, near Naples; in the U. S. from Searles Lake, San Bernardino County, California; in the Green River Formation, Colorado and Utah; in the Tincalayu deposit, Salar del Hombre Muerto, Salta Province, Argentina; on Mt. Alluaiv, Lovozero Massif and Khibiny Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia; and around Mount Erebus, Victoria Land, Antarctica.[3]
References
- ^ Warr, L.N. (2021). "IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols". Mineralogical Magazine. 85 (3): 291–320. Bibcode:2021MinM...85..291W. doi:10.1180/mgm.2021.43. S2CID 235729616.
- ^ a b c Nahcolite on Mindat.org
- ^ a b c Nahcolite in the Handbook of Mineralogy
- ^ a b c Nahcolite data on Webmineral
- ^ Richard V. Gaines, H. Catherine W. Skinner, Eugene E. Foord, Brian Mason, and Abraham Rosenzweig: Dana's new mineralogy, John Wiley & Sons, 1997

