|
 |

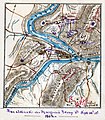
The American Civil War (1861–1865) was a sectional rebellion against the United States of America by the Confederate States, formed of eleven southern states' governments which moved to secede from the Union after the 1860 election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States. The Union's victory was eventually achieved by leveraging advantages in population, manufacturing and logistics and through a strategic naval blockade denying the Confederacy access to the world's markets.
In many ways, the conflict's central issues – the enslavement of African Americans, the role of constitutional federal government, and the rights of states – are still not completely resolved. Not surprisingly, the Confederate army's surrender at Appomattox on April 9,1865 did little to change many Americans' attitudes toward the potential powers of central government. The passage of the Thirteenth, Fourteenth and Fifteenth amendments to the Constitution in the years immediately following the war did not change the racial prejudice prevalent among Americans of the day; and the process of Reconstruction did not heal the deeply personal wounds inflicted by four brutal years of war and more than 970,000 casualties – 3 percent of the population, including approximately 560,000 deaths. As a result, controversies affected by the war's unresolved social, political, economic and racial tensions continue to shape contemporary American thought. The causes of the war, the reasons for the outcome, and even the name of the war itself are subjects of much discussion even today. (Full article)
Wappocomo is a late 18th-century Georgian mansion and farm overlooking the South Branch Potomac River north of Romney, Hampshire County, West Virginia, USA. It is located along Cumberland Road (West Virginia Route 28) and the South Branch Valley Railroad.
The original section of the mansion at Wappocomo was built in 1774 by Nicholas Casey (1745–1833), using bricks that had been used as ballast to stabilize ships loading tobacco in the James River. The Wappocomo property had been a part of the South Branch Survey of Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron's Northern Neck Proprietary. The Parsons family, prominent in Virginia and West Virginia politics in the 18th and 19th centuries, acquired Wappocomo and continue to maintain ownership of the property into the 21st century. (Full article...)

The U.S. state of West Virginia was formed out of western Virginia and added to the Union as a direct result of the American Civil War (see History of West Virginia), in which it became the only modern state to have declared its independence from the Confederacy. In the summer of 1861, Union troops, which included a number of newly formed Western Virginia regiments, under General George McClellan drove off Confederate troops under General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Philippi in Barbour County. This essentially freed Unionists in the northwestern counties of Virginia to form a functioning government of their own as a result of the Wheeling Convention. Before the admission of West Virginia as a state, the government in Wheeling formally claimed jurisdiction over all of Virginia, although from its creation it was firmly committed to the formation of a separate state.
After Lee's departure, western Virginia continued to be a target of Confederate raids. Both the Confederate and state governments in Richmond refused to recognize the creation of the new state in 1863, and thus for the duration of the war the Confederacy regarded its own military offensives within West Virginia not as invasion but rather as an effort to liberate what it considered to be enemy-occupied territory administered by an illegitimate government in Wheeling. Nevertheless, due to its increasingly precarious military position and desperate shortage of resources, Confederate military actions in what it continued to regard as "western Virginia" focused less on reconquest as opposed to both on supplying the Confederate Army with provisions as well as attacking the vital Baltimore and Ohio Railroad that linked the northeast with the Midwest, as exemplified in the Jones-Imboden Raid. Guerrilla warfare also gripped the new state, especially in the Allegheny Mountain counties to the east, where loyalties were much more divided than in the solidly Unionist northwest part of the state. Despite this, the Confederacy was never able to seriously threaten the Unionists' overall control of West Virginia. (Full article...)

Thaddeus Stevens (April 4, 1792 – August 11, 1868) was an American politician and lawyer who served as a member of the United States House of Representatives from Pennsylvania, being one of the leaders of the Radical Republican faction of the Republican Party during the 1860s. A fierce opponent of slavery and discrimination against black Americans, Stevens sought to secure their rights during Reconstruction, leading the opposition to U.S. President Andrew Johnson. As chairman of the House Ways and Means Committee during the American Civil War, he played a leading role, focusing his attention on defeating the Confederacy, financing the war with new taxes and borrowing, crushing the power of slave owners, ending slavery, and securing equal rights for the freedmen.
Stevens was born in rural Vermont, in poverty, and with a club foot, which left him with a permanent limp. He moved to Pennsylvania as a young man and quickly became a successful lawyer in Gettysburg. He interested himself in municipal affairs and then in politics. He was an active leader of the Anti-Masonic Party, as a fervent believer that Freemasonry in the United States was an evil conspiracy to secretly control the republican system of government. He was elected to the Pennsylvania House of Representatives, where he became a strong advocate of free public education. Financial setbacks in 1842 caused him to move his home and practice to the larger city of Lancaster. There, he joined the Whig Party and was elected to Congress in 1848. His activities as a lawyer and politician in opposition to slavery cost him votes, and he did not seek reelection in 1852. After a brief flirtation with the Know-Nothing Party, Stevens joined the newly formed Republican Party and was elected to Congress again in 1858. There, with fellow radicals such as Massachusetts Senator Charles Sumner, he opposed the expansion of slavery and concessions to the South as the war came. (Full article...)
- ... that Francis Orray Ticknor was a country doctor whose fame as a poet relies on "Little Giffen", a poem about one of his patients who died in the American Civil War?
- ... that CSS Beaufort fought USS Albatross in the first ship-versus-ship action of the American Civil War?
- ... that Emma Dean Powell received a pass from General Ulysses S. Grant to accompany her husband to battlefield camps during the American Civil War after he lost his arm?
- ... that after the Little Rock campaign, Union forces held three-quarters of Arkansas?
- ... that according to one historian, James S. Rains made a "significant contribution to the Confederate war effort" by getting drunk?
- ... that The Land We Love, a little magazine that merged into Southern Magazine, printed American Civil War recollections, poetry, agricultural material, and many works by female authors?
- Attention needed
- ...to referencing and citation • ...to coverage and accuracy • ...to structure • ...to grammar • ...to supporting materials
- Popular pages
- Full list
- Cleanup needed
- The West Tennessee Raids
- Requested articles
- James Ashby (soldier) • Bluffton expedition • Benjamin D. Fearing • Charles A. Hickman • Richard Henry Jackson • James B. Speers • Charles S. Steedman • Battle of Barton's Station • Lawrence P. Graham • Thomas John Lucas • Daniel Henry Rucker • James Hughes Stokes • Frederick S. Sturmbaugh • Davis Tillson • Action at Nineveh (currently a redirect) • International response to the American Civil War • Spain and the American Civil War • Savannah Campaign Confederate order of battle • Native Americans in the American Civil War (currently disambiguation after deletion) • 1st Battalion, Mississippi Mounted Rifles (Union) • Battle of Lafayette • Requested American Civil War Medal of Honor recipients
- Expansion needed
- Battle of Boonsborough • Battle of Guard Hill • Battle of Rice's Station • Battle of Simmon's Bluff • Battle of Summit Point • Charleston Arsenal • Edenton Bell Battery • First Battle of Dalton • Blackshear Prison • Edwin Forbes • Hiram B. Granbury • Henry Thomas Harrison • Louis Hébert (colonel) • Benjamin G. Humphreys • Maynard Carbine • Hezekiah G. Spruill • Smith carbine • Edward C. Walthall • Confederate States Secretary of the Navy • Confederate States Secretary of the Treasury • David Henry Williams • Battle of Rome Cross Roads • Delaware in the American Civil War • Ironclad Board • United States Military Railroad • Kansas in the American Civil War • Rufus Daggett • Ebenezer Magoffin • Confederate Quartermaster-General's Department • First Corps, Army of Northern Virginia • Francis Laurens Vinton • Henry Maury • Smith's Expedition to Tupelo • Other American Civil War battle stubs • Other American Civil War stubs
- Images needed
- Battle of Lone Jack • Preston Pond, Jr. • Melancthon Smith
- Merging needed
- 1st Regiment New York Mounted Rifles and 7th Regiment New York Volunteer Cavalry
- Citations needed
- 1st Alabama Cavalry Regiment (Union) • 4th Maine Battery • 33rd Ohio Infantry • 110th New York Volunteer Infantry • Battle of Hatcher's Run • Camp Dennison • Confederate colonies • CSS Resolute • Dakota War of 1862 • Florida in the American Civil War • Ethan A. Hitchcock (general) • Fort Harker (Alabama) • Gettysburg (1993 film) • Iowa in the American Civil War • Second Battle of Fort Sumter • Samuel Benton
- Translation needed
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-

-

-

-

-
Random portal
- Shortcuts to this page: Portal:ACW • P:ACW