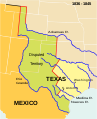
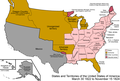
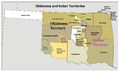
The Oklahoma Portal Oklahoma (/ˌoʊkləˈhoʊmə/ ⓘ OHK-lə-HOH-mə; Choctaw: Oklahumma, pronounced [oklahómma]; Cherokee: ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, Okalahoma, pronounced [ògàlàhǒːmã́]) is a landlocked state in the South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northeast, Arkansas to the east, New Mexico to the west, and Colorado to the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the 20th-most extensive and the 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw words okla, 'people' and humma, which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its nickname, "The Sooner State", in reference to the Sooners, settlers who staked their claims in formerly American Indian-owned lands until the Indian Appropriations Act of 1889 authorized the Land Rush of 1889 opening the land to white settlement. With ancient mountain ranges, prairie, mesas, and eastern forests, most of Oklahoma lies in the Great Plains, Cross Timbers, and the U.S. Interior Highlands, all regions prone to severe weather. Oklahoma is at a confluence of three major American cultural regions. Historically, it served as a government-sanctioned territory for American Indians moved from east of the Mississippi River, a route for cattle drives from Texas and related regions, and a destination for Southern settlers. There are currently 26 spoken in Oklahoma. According to the 2020 U.S. census, 14.2 percent of Oklahomans identify as American Indians, the highest indigenous population by percentage in any state. A major producer of natural gas, oil, and agricultural products, Oklahoma relies on an economic base of aviation, energy, telecommunications, and biotechnology. Oklahoma City and Tulsa serve as Oklahoma's primary economic anchors, with nearly two-thirds of Oklahomans living within their metropolitan statistical areas. (Full article...) Selected article -Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States government for the relocation of Native Americans who held original Indian title to their land as an independent nation-state. The concept of an Indian territory was an outcome of the U.S. federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the U.S. government was one of assimilation. Indian Territory later came to refer to an unorganized territory whose general borders were initially set by the Nonintercourse Act of 1834, and was the successor to the remainder of the Missouri Territory after Missouri received statehood. The borders of Indian Territory were reduced in size as various Organic Acts were passed by Congress to create organized territories of the United States. The 1907 Oklahoma Enabling Act created the single state of Oklahoma by combining Oklahoma Territory and Indian Territory, annexing and ending the existence of an unorganized independent Indian Territory as such, and formally incorporating the tribes and residents into the United States. (Full article...)Spotlight city -Norman (/ˈnɔːrmən/) is the 3rd most populous city in the U.S. state of Oklahoma, with a population of 128,026 as of the 2020 census. It is the most populous city and the county seat of Cleveland County and the second-most populous city in the Oklahoma City metropolitan area after the state capital, Oklahoma City, 20 miles (32 kilometers) north of Norman. The city was settled during the Land Run of 1889, which opened the former Unassigned Lands of Indian Territory to American pioneer settlement. It was named in honor of Abner Norman, the area's initial land surveyor, and was formally incorporated on May 13, 1891. Norman has prominent higher education and related research industries, as it is home to the University of Oklahoma, the largest university in the state, with nearly 32,000 students. The university is well known for its sporting events by teams under the banner of the nickname "Sooners", with over 85,000 people routinely attending football games. The university is home to several museums, including the Fred Jones Jr. Museum of Art, which contains the largest collection of French Impressionist art ever given to an American university, as well as the Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History. (Full article...)Selected picture Credit: User:CPacker Seminary Hall served as the main building for the Cherokee Female Seminary from 1889 to 1909. Featured content
Featured lists: Oklahoma birds • Tallest buildings in Tulsa • List of tallest buildings in Oklahoma City • List of birds of Oklahoma • List of Oklahoma Sooners football seasons • List of Oklahoma Sooners head football coaches • List of Oklahoma Sooners in the NFL Draft State facts
State symbols
Selected biography -Vincent Grant Gill (born April 12, 1957) is an American country, bluegrass, and rock singer, songwriter, and musician. He began in a number of local bluegrass bands in the 1970s, and from 1978 to 1982, he achieved his first mainstream attention as lead singer of the soft rock band Pure Prairie League. After leaving that band, Gill served as a backing musician for Rodney Crowell before beginning a solo career in 1984. Gill recorded for RCA Records Nashville from then until 1988. A year later, he signed with MCA Nashville, where he would have his country music breakthrough with When I Call Your Name between then and 1990. Gill has remained with MCA for all subsequent albums. His commercial peak came in the first half of the 1990s, starting with his breakthrough album When I Call Your Name. Gill has 65 entries on the Billboard Hot Country Songs charts, including four solo number one hits: "I Still Believe in You", "Don't Let Our Love Start Slippin' Away", "One More Last Chance", and "Tryin' to Get Over You", all between 1992 and 1994. He has also had number-one singles as a guest on Reba McEntire's "The Heart Won't Lie" (1993), Chris Young's "Sober Saturday Night" (2016-17), and the multi-artist collaboration "Forever Country" (2016). All of Gill's albums released in the 1990s were certified platinum or higher by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA), with the highest being 1992's I Still Believe in You at quintuple-platinum. Gill has won 22 Grammy Awards, the most among solo male country music artists. (Full article...)Did you know -
General images -The following are images from various Oklahoma-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related portalsWikiprojects
Things you can do
Oklahoma topicsCategoriesNew articlesThis list was generated from these rules. Questions and feedback are always welcome! The search is being run daily with the most recent ~14 days of results. Note: Some articles may not be relevant to this project.
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2024-04-24 22:09 (UTC) Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|

Sons of Union Veterans of the Civil War









![Image 5Cartoonist's rendering of Theodore Roosevelt's initial reaction to the Oklahoma Constitution.[needs context] (from History of Oklahoma)](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/2/28/Teddyrooseveltoklahomaconstitution.png/120px-Teddyrooseveltoklahomaconstitution.png)