Contents
Rhodocactus is a genus of flowering plant in the cactus family Cactaceae, native to central South America.[2] Unlike most species of cacti, Rhodocactus has persistent leaves and a fully tree-like habit. The genus was sunk into a broadly circumscribed Pereskia, but molecular phylogenetic studies from 2005 onwards showed that with this circumscription Pereskia was paraphyletic, and in 2016, Rhodocactus was restored for southern South American species.
Description
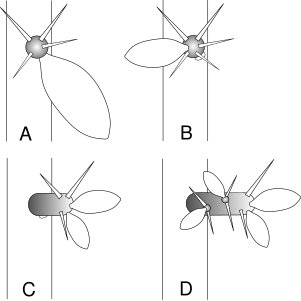
Like all cacti, Rhodocactus species have a succulent habit and specialized structures, areoles, that bear spines. They differ from most cacti in having persistent leaves. They grow as trees, 3–7 m (10–23 ft) tall. When mature, their stems develop bark, but its development is delayed, and all the species other than Rhodocactus nemorosus retain stomata. The areoles of Rhodocactus species can form "brachyblasts",[3] called "spur shoots" by Beat Leuenberger. The areole initially forms in the axil of a leaf (stage A in the diagram below). This leaf may be lost, leaving a leaf scar, and leaves may grow on the areole (stage B). The areole may then grow out to form a brachyblast – a short, very crowded shoot that bears leaves (stage C). Later this may form a longer, but still short shoot that has its own areoles (stage D).[4] Asai and Miyata regard the formation of brachyblast leaves as a distinguishing characteristic of the genus in comparison to Pereskia.[3] Rhodocactus flowers are about 3–5 cm (1.2–2.0 in) in diameter.[3]
-
Areole and brachyblast development in Rhodocactus
-
Areole on a young stem of R. grandiflorus is in the axis of the auxoblast leaf (stage A)
-
Areoles on this stem of R. grandiflorus have brachyblast leaves (stage B)
-
Short shoot of R. grandiflorus (stage D)
Taxonomy
Rhodocactus was originally described as a subgenus of Pereskia by Alwin Berger, and was raised to a genus in 1936 by Frederik Marcus Knuth.[1][3] The genus was later sunk back into in a broadly defined genus Pereskia. Molecular phylogenetic studies from 2005 onwards suggested that when circumscribed in this way, Pereskia was not monophyletic, and consisted of three clades.[5][6][3] By 2016, each clade was recognized as a separate genus, one of which is Rhodocactus. Only the type species of Knuth's circumscription of the genus, Rhodocactus grandifolius, belongs to the clade re-described as Rhodocactus. The other species were mostly newly transferred from Pereskia.[3]
A consensus cladogram from a 2005 study is shown below with the more recent generic assignments added. It shows that the three genera are basal to the rest of the cacti.[5]
|
Pereskia as previously defined |
Species
As of April 2021, Plants of the World Online accepted the following species:[2]
| Image | Scientific name | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
 |
Rhodocactus bahiensis (Gürke) I.Asai & K.Miyata< | Brazil |
 |
Rhodocactus grandifolius (Haw.) F.M.Knuth | eastern and southern Brazil. |
 |
Rhodocactus nemorosus (Rojas Acosta) I.Asai & K.Miyata | Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and northeast Argentina. |
 |
Rhodocactus sacharosa (Griseb.) Backeb. | Bolivia and west-central Brazil to Paraguay and northern Argentina |
 |
Rhodocactus stenanthus (F.Ritter) I.Asai & K.Miyata | Brazil |
Species that have also been placed in Rhodocactus include:[3]
- Rhodocactus bleo (F.M.Knuth) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria bleo F.M.Knuth) Lodé
- Rhodocactus guamacho (F.A.C.Weber) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria guamacho (F.A.C.Weber) Lodé
- Rhodocactus horridus (DC.) F.M.Knuth = Pereskia horrida D.C.
- Rhodocactus lychnidiflorus (D.C.) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria lychnidiflora (D.C.) Lodé
- Rhodocactus portulacifolius (L.) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria portulacifolia (L.) Lodé
- Rhodocactus zinniiflorus (D.C.) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria zinniiflora (D.C.) Lodé
References
- ^ a b "Rhodocactus (A.Berger) F.M.Knuth", The International Plant Names Index, retrieved 2021-04-25
- ^ a b "Rhodocactus (A.Berger) F.M.Knuth", Plants of the World Online, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, retrieved 2021-04-25
- ^ a b c d e f g Asai, Issaku & Miyata, Kazunori (2016), "An Emendation of Rhodocactus, a Genus Segregated from Pereskia (Cactaceae)" (PDF), Journal of Japanese Botany, 91: 7–12, archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-07-11, retrieved 2021-04-25
- ^ Leuenberger, Beat Ernst (1986), Pereskia (Cactaceae), Memoirs of the New York Botanical Garden, vol. 14, Bronx, NY: New York Botanical Garden, p. 11, ISBN 978-0-89327-307-1, retrieved 2021-05-02
- ^ a b Edwards, Erika J.; Nyffeler, Reto & Donoghue, Michael J. (2005), "Basal cactus phylogeny: implications of Pereskia (Cactaceae) paraphyly for the transition to the cactus life form", American Journal of Botany, 92 (7): 1177–1188, doi:10.3732/ajb.92.7.1177, PMID 21646140
- ^ Bárcenas, Rolando T.; Yesson, Chris & Hawkins, Julie A. (2011), "Molecular systematics of the Cactaceae", Cladistics, 27 (5): 470–489, doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.2011.00350.x, PMID 34875796, S2CID 83525136