Welcome to the Bosnia and Herzegovina Portal
 |
 |
| |
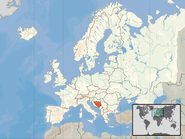
Bosnia and Herzegovina (Serbo-Croatian: Bosna i Hercegovina, Босна и Херцеговина), sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe, situated on the Balkan Peninsula. It borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest. In the south it has a 20 kilometres (12 miles) long coast on the Adriatic Sea, with the town of Neum being its only access to the sea. Bosnia has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. In the central and eastern regions, the geography is mountainous, in the northwest it is moderately hilly, and in the northeast it is predominantly flat. Herzegovina, the smaller, southern region, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous. Sarajevo is the capital and the largest city.
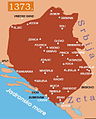
The area has been inhabited since at least the Upper Paleolithic, but evidence suggests that during the Neolithic age, permanent human settlements were established, including those that belonged to the Butmir, Kakanj, and Vučedol cultures. After the arrival of the first Indo-Europeans, the area was populated by several Illyrian and Celtic civilizations. The ancestors of the South Slavic peoples that populate the area today arrived during the 6th through the 9th century. In the 12th century, the Banate of Bosnia was established; by the 14th century, this had evolved into the Kingdom of Bosnia. In the mid-15th century, it was annexed into the Ottoman Empire, under whose rule it remained until the late 19th century; the Ottomans brought Islam to the region. From the late 19th century until World War I, the country was annexed into the Austro-Hungarian monarchy. In the interwar period, Bosnia and Herzegovina was part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. After World War II, it was granted full republic status in the newly formed Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. In 1992, following the breakup of Yugoslavia, the republic proclaimed independence. This was followed by the Bosnian War, which lasted until late 1995 and ended with the signing of the Dayton Agreement.
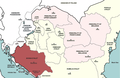
The country is home to three main ethnic groups: Bosniaks are the largest group, Serbs the second-largest, and Croats the third-largest. Minorities include Jews, Roma, Albanians, Montenegrins, Ukrainians and Turks. Bosnia and Herzegovina has a bicameral legislature and a three-member presidency made up of one member from each of the three major ethnic groups. However, the central government's power is highly limited, as the country is largely decentralized. It comprises two autonomous entities—the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska—and a third unit, the Brčko District, which is governed by its own local government.
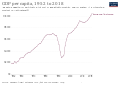
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a developing country and ranks 74th in the Human Development Index. Its economy is dominated by industry and agriculture, followed by tourism and the service sector. Tourism has increased significantly in recent years. The country has a social-security and universal-healthcare system, and primary and secondary level education is free. It is a member of the UN, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, the Council of Europe, the Partnership for Peace, and the Central European Free Trade Agreement; it is also a founding member of the Union for the Mediterranean, established in July 2008. Bosnia and Herzegovina is an EU candidate country and has also been a candidate for NATO membership since April 2010. (Full article...)
Selected article -
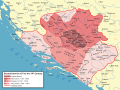
The siege of Sarajevo (Bosnian: Opsada Sarajeva) was a prolonged blockade of Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia and Herzegovina, during the Bosnian War. After it was initially besieged by the forces of the Yugoslav People's Army, the city was then besieged by the Army of Republika Srpska. Lasting from 5 April 1992 to 29 February 1996 (1,425 days), it was three times longer than the Battle of Stalingrad, more than a year longer than the siege of Leningrad, and was the longest siege of a capital city in the history of modern warfare.
When Bosnia and Herzegovina declared independence from Yugoslavia after the 1992 Bosnian independence referendum, the Bosnian Serbs—whose strategic goal was to create a new Bosnian Serb state of Republika Srpska (RS) that would include Bosniak-majority areas—encircled Sarajevo with a siege force of 13,000 stationed in the surrounding hills. From there they assaulted the city with artillery, tanks, and small arms. From 2 May 1992, the Serbs blockaded the city. The Bosnian government defence forces (ARBiH) inside the besieged city, approximately with 34,931 troops on average, without heavy weapons or armor, defended much of the urban area of the city throughout the war but were unable to break the siege. The siege was lifted following the signing of the Dayton Agreement on December 14th, 1995. A total of 13,952 people were killed during the siege, including 5,434 civilians. The ARBiH sustained 3,587 fatalities, while Bosnian Serb military casualties numbered 2,241 killed soldiers. The 1991 census indicates that before the siege, the city and its surrounding areas had a total population of 525,980. According to some estimates, the total population of the city proper prior to the siege was 435,000. Estimates of the population of Sarajevo after the siege ranged from 300,000 to 380,000. Sarajevo's population endured up to six months without gas, electricity or water supply during certain stages of the siege. (Full article...)General images
More did you know
- ... that to receive a work permit to play in Luxembourg, Bosnian footballer Sanel Ibrahimović had to pretend to be a specialist in his country's cuisine?
Cities
- Banja Luka
- Bihać
- Berkovići
- Bijeljina
- Bosanska Krupa
- Bosanski Petrovac
- Brčko
- Brod
- Bugojno
- Cajnice
- Cazin
- Derventa
- Doboj
- Donji Vakuf
- Dubica
- Foča
- Goražde
- Gornji Vakuf
- Gračanica
- Gradačac
- Gradiška
- Ilidža
- Istočno Sarajevo
- Jajce
- Jablanica
- Kakanj
- Kalesija
- Konjic
- Kotor Varoš
- Laktaši
- Livno
- Ljubuški
- Lukavac
- Modriča
- Mostar
- Nevesinje
- Neum
- Novi Grad
- Novi Travnik
- Olovo
- Petrovo
- Prijedor
- Prnjavor
- Sanski Most
- Sarajevo
- Srebrenik
- Srebrenica
- Teslić
- Tešanj
- Travnik
- Trebinje
- Tuzla
- Velika Kladuša
- Visoko
- Vitez
- Zavidovići
- Zenica
- Zvornik
- Živinice
- Žepče
Selected biography -
Catherine of Bosnia (Serbo-Croatian: Katarina Kosača/Катарина Косача; 1424/1425 – 25 October 1478) was Queen of Bosnia as the wife of King Thomas, the penultimate Bosnian sovereign. She was born into the powerful House of Kosača, staunch supporters of the Bosnian Church. Her marriage in 1446 was arranged to bring peace between the King and her father, Stjepan Vukčić. The queenship of Catherine, who at that point converted to Roman Catholicism, was marked with an energetic construction of churches throughout the country.
Following her husband's death in 1461, Catherine's role receded to that of queen dowager at the court of her stepson, King Stephen Tomašević. Two years later, forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Mehmed the Conqueror invaded Bosnia and put an end to the independent kingdom. Catherine's stepson was executed, while Sigismund and Catherine, her son and daughter by Thomas, were captured and taken to Constantinople, where they converted to Islam. Queen Catherine escaped, taking refuge in Dubrovnik and eventually settling in Rome, where she received a pension from the papacy. From Rome she strove to be reunited with her children. Her efforts to negotiate and offer a ransom proved futile. She died a Franciscan tertiary in Rome, having named the papacy guardians of Bosnia and her children heirs to the throne, should they ever return to Christianity. (Full article...)List of selected biographies
|
|---|
Did you know (auto-generated)

- ... that Ivan Ančić was the first Bosnian Franciscan to use the Latin script to write in his native language?
- ... that a Socialist Youth League candidate in the 1990 Bosnian general election registered his ethnicity as 'Eskimo' as an apparent protest against ethnic registry requirements for candidates?
Subcategories
Related portals
Religions in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Ex-Yugoslav countries
Other countries
Topics
Recognized content
Things you can do

- Request images:
- Request maps:
- Sarajevo city location map
- Articles wanted:
- Clinical Center University of Sarajevo (Koševo hospital);
- Articles needing major work, Be Bold!: **
- Architecture of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Health in Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Literature of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- List of universities in Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Foreign relations of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Cinema of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Subpages of List of settlements in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Stubs needing expansion:
- Featured Portals:
- Featured Pictures:
- Articles with Featured Article Candidate's status within reach:
- Current Featured Candidates:
- Featured Articles: (Don't be too bold!)
- Current Good Article Candidates:
- Good Articles:
- Former Good Articles:
Web resources
- B&H Tourism - Official Web Site
- Tourism Association of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina - Official Web Site
- Tourism Association of Republika Srpska - Official Web Site
- Duga-Tehna
Other links:
- Bosnian National Monument - Muslibegovica House
- "Bosnia and Herzegovina". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Bosnia & Herzegovina Economy
- Bosnia and Herzegovina Map
- Bosnia News
- rjecnik.ba English-Bosnian and German-Bosnian On-line Dictionary (in Bosnian, English, and German)
- The State of Media Freedom in Bosnia and Herzegovina: The Public Service Broadcasting Report by the OSCE Representative on Freedom of the Media
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-

-

-

-

-
Random portal
Purge server cache